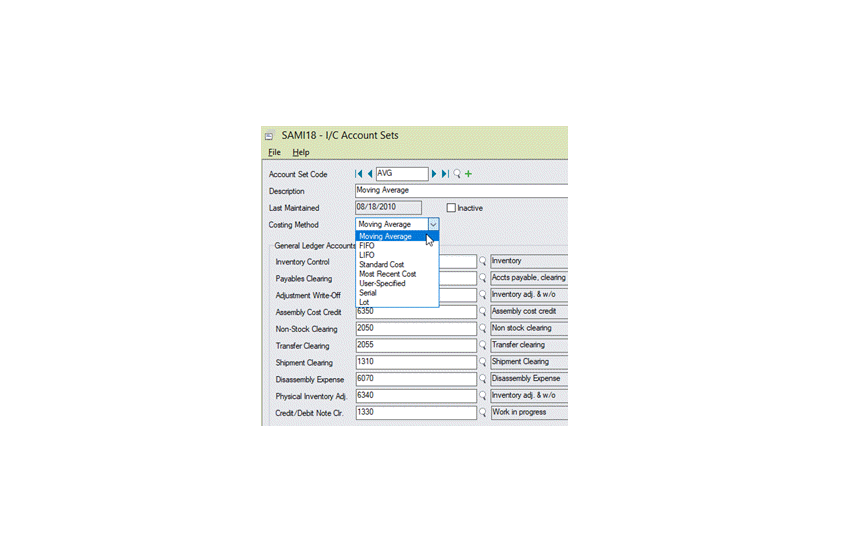
Different costing methods can be used to value inventory and determine cost of goods sold in Sage 300 Inventory Control. The costing method is assigned to Account Sets (IC Options / Account Sets), and account sets are assigned to items.
Therefore, it is possible to have different items being costed in different ways. Following is a brief overview of the most common costing methods:
- Moving Average: Inventory Control combines the costs of all items at an individual location, so that the costs of one item are not able to be identified from the costs of another. The unit cost of an item is the total cost of all items in the location divided by the total quantity of items at the location – at that specific point in time.
- It is the simplest costing method
- Default cost on order is moving average, actual COGs cost is moving average, and cost removed from inventory is also moving average.
- Inventory is valued at an average cost of all received items (that are on hand at that point in time)
- Current revenues are matched with the average cost of all items on hand at that point in time.
 Most Recent: Inventory Control assigns the cost of the most recently received item at the location to all items shipped.
Most Recent: Inventory Control assigns the cost of the most recently received item at the location to all items shipped.
- Default cost on order is most recent cost, actual COGs is most recent cost, and cost removed from inventory is the moving average cost. Variance between most recent and average cost is posted to the cost variance account
- Closing inventory values are from the oldest costs
- Current revenues are matched with current costs
- FIFO(First In First Out): Inventory Control assumes that the first units to arrive at a location are the first units shipped. In this way, stock is rotated; old stock is shipped, new stock is stored.
- Default cost on order is moving average, actual COGs cost is FIFO, and cost removed from inventory is also the FIFO amount.
- Closing inventory values are from the most recent purchases
- Current revenues are matched with older costs
- Note – offset bucket may cause issues with costing in this method for any items going into negative inventory or adjustments not posted to specific buckets.
- LIFO(Last In First Out): Inventory Control assumes that the last units to arrive at a location are the first ones shipped. Stock is not rotated; new stock is sold as soon as it arrives and older stock may sit for long periods, until all stock is shipped.
- Default cost on order is moving average, actual COGs cost is LIFO, and cost removed from inventory is also the LIFO amount.
- Closing inventory values are from the oldest purchases – which may no longer be accurate, depending on how quickly stock is moving through warehouse and if all items are ever cleared out.
- Current revenues are matched to current costs.
- Note – as with the FIFO method, offset bucket may cause issues with costing in this method for any items going into negative inventory or adjustments not posted to specific buckets.
- Standard: Standard costs can be predetermined targets that are useful in building budgets and gauging performance. This method might be used if the item costs do not vary much, or if stock turnover is rapid.
- Must be manually entered (or imported) through the Location Details screen
- Default cost on order is standard cost, actual COGs is standard cost, and cost removed from inventory is the moving average cost. Variance between standard and average is posted to cost variance account
- Actual costs are posted to inventory upon receipt. Inventory is valued (for unit cost) using moving average costing
- Current revenues are matched with a fixed, pre-specified standard cost.
- User-Specified: User-specified costing allows the user to enter costs for items as they are shipped. It is mandatory to use this costing method for all non-stock items but it can also be used for stock items.
- Default cost on order is most recent cost, actual COGs is user specified (or MRC if user does not change it), and cost removed from inventory is the user-specified cost (or MRC if user does not change it).
- Inventory is received at actual cost and valued (for unit cost) at moving average.
- Current revenues are matched to a user-specified cost (or most recent cost), therefore current costs.
For a more detailed review of these and other costing methods, check out our training session on Inventory Control Costing Methods and other topics by scrolling to the bottom of our training page. You can also see another blog post on the Difference between Last Cost and Most Recent Cost Still have questions? Give us a call at 866-436-3530 or email support@equationtech.us. We’re here to help!
 Most Recent: Inventory Control assigns the cost of the most recently received item at the location to all items shipped.
Most Recent: Inventory Control assigns the cost of the most recently received item at the location to all items shipped.